issue contents
October 2009 issue

Cover illustration: Though cyclohexanol is a simple compound it has a rich phase diversity at low temperature. It forms a disordered glassy phase on cooling, but this can be transformed into ordered phases (II), (III) and the metastable (III'), which all have different hydrogen-bonding motifs. The series of transitions is attributable to the conformational flexibility of the hydroxyl group [Ibberson et al. (2008). Acta Cryst. B64, 573-582].
research papers






















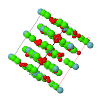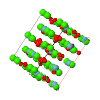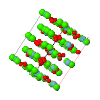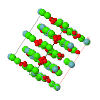
Topological analyses of the experimental electron-density distributions in crystals of five chain polymers [M(μ-X)2(py)2] (M = Zn, Cd; X = Cl, Br; py = 3,5-substituted pyridine) confirmed the existence of (3, −1) critical points both for intuitively strong chemical bonds and for secondary interactions. The latter comprise intra- and inter-strand C—H⋯X—M hydrogen bonds and C—X⋯X—C interhalogen contacts and stabilize the polymeric structures unusual for Zn as the metal center.


 access
access





 journal menu
journal menu