issue contents
April 2007 issue

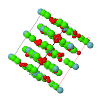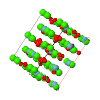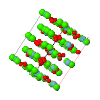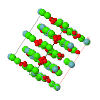
Cover illustration: The cover illustration represents the high- and incommensurately modulated room-temperature phases of Na2CO3 and its reconstructed reciprocal (h2lm) layer (![[gamma]](/logos/entities/gamma_rmgif.gif) -Na2CO3; Dusek et al. (2003). Acta Cryst. B59, 337-352]. Main reflections (open circles) and satellites aligned along parallel lines are indicated. A comparison of the two structures represented by slices parallel to the vertical axis c illustrates their relationship [Arakcheeva & Chapuis (2005). Acta Cryst. B61, 601-607].
-Na2CO3; Dusek et al. (2003). Acta Cryst. B59, 337-352]. Main reflections (open circles) and satellites aligned along parallel lines are indicated. A comparison of the two structures represented by slices parallel to the vertical axis c illustrates their relationship [Arakcheeva & Chapuis (2005). Acta Cryst. B61, 601-607]. ![[beta]](/logos/entities/beta_rmgif.gif) -Na2CO3 at 746 K (C2/m; pseudohexagonal) is shown on the left. All C and Na atoms closer than 3.12 Å are linked. The corresponding non-periodic slice of
-Na2CO3 at 746 K (C2/m; pseudohexagonal) is shown on the left. All C and Na atoms closer than 3.12 Å are linked. The corresponding non-periodic slice of ![[gamma]](/logos/entities/gamma_rmgif.gif) -Na2CO3 indicates how the modulation creates additional close contacts (Ivan Orlov's design is kindly acknowledged).
-Na2CO3 indicates how the modulation creates additional close contacts (Ivan Orlov's design is kindly acknowledged).
research papers


























 journal menu
journal menu