issue contents
June 2006 issue

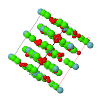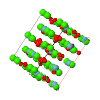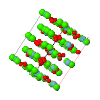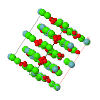
Cover illustration: Room-temperature structure of the cation-deficient perovskite, Nd0.7Ti0.9Al0.1O3 [Zhang et al. (2006). Acta Cryst. B62, 60-67>]. The superlattice peaks associated with out-of-phase octahedral tilting (shown) have intensities consistent with tilting around the x and y axes (sum of a- and c-), but tilting around the y axis (contribution b-) evidently does not occur. The tilt system in Glazer's notation is thus a-b0c-, and the space group and structure are found from the tree displayed. Two views of the structure are shown - the (TiAl)O6 are shown as octahedra, the Ti/Al atom being visible within them, and the darker and lighter spheres outside these octahedra represent fully and partly occupied layers of Nd, respectively. The octahedral tilting, around both x and y axes, is clearly seen.
feature articles

research papers










 access
access





 access
access





 journal menu
journal menu